C++ Dynamic Ambience and Smart Surface awareness (player PoV)
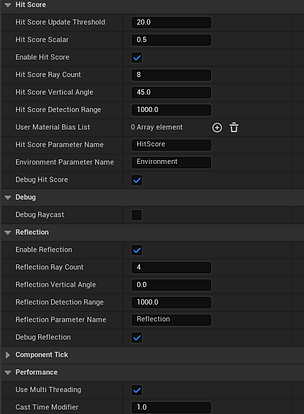
This custom component UAudioHitScoreBase implements a real-time environmental parameterisation system that uses periodic multi-threaded raycasting to analyse the spatial geometry and surface properties surrounding an Actor. It performs two distinct sets of line traces: one to derive a HitScoreValue, quantifying the spatial enclosure/openness, and another for a ReflectionValue, indicating acoustic reflectivity. Material data gleaned from FHitResult objects, particularly UMaterialInterface and material names, is processed to determine a DominantEnvironment. This aggregate environmental data (HitScoreValue, ReflectionValue, and DominantEnvironment) is then exposed to audio middleware. The derived UAudioHitScore component acquires an FMOD Studio EventInstance via FMOD::Studio::System::getEvent and dynamically updates its corresponding middleware parameters (e.g., "HitScore", "Reflection", "Environment") at a configurable interval using setParameterByName. This system, with its FScopeLock for thread-safe data access and integration with the Lyra Experience system for deferred initialisation, demonstrates a robust approach to procedural audio spatialisation and material-based acoustic simulation within a game engine.
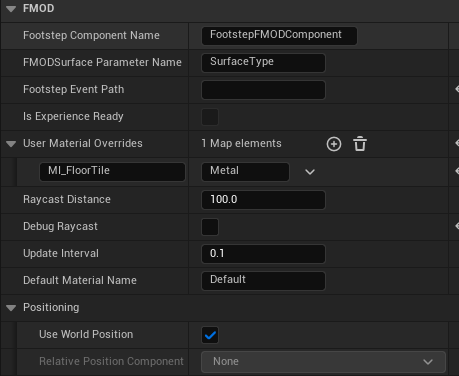
The USmartSurfaceBase component continually performs a downward raycast from its owning actor, identifying the underlying surface material at a set UpdateInterval. It processes the FHitResult to retrieve material names, with support for designer-defined overrides. The detected material's name is then broadcast via a delegate (OnSurfaceMaterialDetected).
Derived components, USmartSurface_Player and USmartSurface_Enemy, subscribe to this delegate. Upon material detection, they translate the material name (e.g., "Wood", "Metal") into a corresponding numerical value. This value is subsequently applied as a parameter to an attached UAudioComponent using SetParameter, dynamically influencing the audio event's playback.
For multiplayer environments, USmartSurface_Player incorporates server-replicated footstep playback logic, utilising RPCs (Server_PlayFootstepSound_Implementation, Multicast_PlayFootstepSound_Implementation, Client_PlayTeammateFootstepSound_Implementation) to ensure consistent, synchronized footstep audio and material parameters across all networked clients. This architecture enables highly responsive and acoustically varied footstep sounds based on dynamic surface interaction.
prototyping Line-of-Sight detection
This custom-built UAudioToolsLOS system provides a robust solution for real-time Line-of-Sight (LOS) detection between game objects to dynamically set occlusion parameters. It identifies if a clear path exists between a listener and an emitter using a multi-line raycasting system with user-configurable width to evaluate if any intervening geometry obstructs the direct line, thereby allowing for the creation of a percentage value of occlusion to account for partial blockages. Furthermore, the system detects and passes the world materials of blocking objects as middleware parameters, enabling custom occlusion characteristics based on the perceived thickness and acoustic properties of the obstructing material.
The system dynamically identifies potential sound emitters within a configurable detection radius using a broad-phase sphere trace. For each detected emitter, a LOS query is initiated. The trace results, detailing whether the path is clear or blocked and by what material, are then fed back into the audio pipeline to dynamically update parameters on the corresponding audio event. This seamless, real-time integration of spatial awareness with audio middleware allows for highly convincing acoustic behaviours that react realistically to the game world's geometry and material composition.
To maintain performance, the system employs asynchronous execution, offloading computationally intensive raycasting operations to a dedicated background thread. This concurrent processing ensures that the main game thread remains unblocked, preserving game responsiveness.
C# Volume Detection and Dynamic Ambience
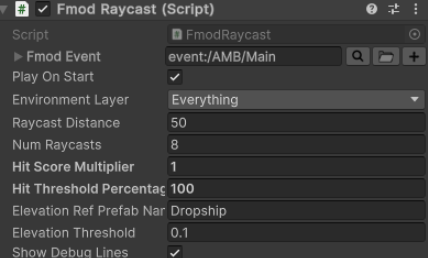
This C# script, FmodRaycast, acts as an environmental audio spatialisation component in Unity, dynamically influencing FMOD parameters based on the surrounding geometry. At a regular checkInterval, it performs multiple raycasts (configured by numRaycasts and raycastDistance) from its object to detect nearby surfaces within a specified environmentLayer. From these raycast results, it calculates a "Hit Score" parameter, which quantifies the density or enclosure of the environment, and sets it on the global FMOD Studio System. Additionally, the script calculates and updates an "Elevation" parameter based on the object's vertical position relative to a designated reference prefab, ensuring this parameter is only updated when a significant change in elevation occurs. Debug lines are optionally displayed to visualise the raycasts and calculated positions, aiding in authoring and verification.
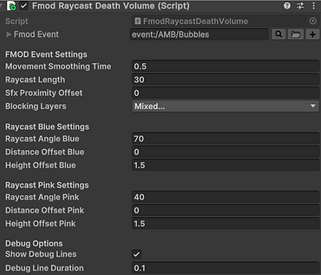
The FmodRaycastDeathVolume C# script in Unity is designed to trigger and control an FMOD event when the object it's attached to nears a "Death Volume" within the game. This component continually scans for objects by casting multiple raycasts (configured with distinct "Blue" and "Pink" settings for angle, offset, and height) from its position. If any of these rays intersect with a DeathVolume collider, the script initiates or sustains an associated FMOD event. The sound's 3D attributes, including its position, are dynamically updated to originate from the averaged hit point of the raycasts, allowing for spatially accurate audio cues. The FMOD event's "Hits" parameter is also updated based on the number of successful raycasts, providing granular control over the audio's intensity or characteristics. If no "Death Volume" is detected, the FMOD event is gracefully stopped with a fade-out. Debug visualisations are included to aid in setting up and verifying the raycast behaviour.
Matt McGuinness showreel
'Terratech Worlds' audio systems
The Tech event includes parameters such as Speed, Surface, Mass, Turn, Brake, Load, Throttle, WheelForce, WheelType, WheelCount, CabType, Spray, and Biome strings to shape it according to player setup, driving physics and environmental factors.
The Ambience event receives TimeofDay and Biome strings for atmos/creature variation throughout the day/night cycle. Other variables handle procedural factors such as WindSpeed, WaterDepth, WaterWaves, HeightAboveWater, HeightAboveGround, Altitude, and Storm.
It uses built-in Event Orientation with Axis automation to rotate Quad sources around 360 degrees.
Pirate Queen: VR Sound Design
(built for Oculus Rift in UE4.26, FMOD and Reaper)
This interactive VR experience puts the player in the body of the most successful pirate in history - the notorius Ching Shih. Guided by both narration and the spirit of her late husband Zheng Yi, the player must escape the pirate cabin they find themselves held captive in by searching for clues, keys, daggers and locks to discover the hidden trapdoor.
Role of sound in Pirate Queen:
-
scale out the visual world with ambisonics and provide audio easter eggs
-
subconsciously steer the player's focus through the narrative in a personal way
-
add satisfaction, weight and realism to all interactions with the various VR objects
-
exploit the Oculus software and hardware to provide accurate HRTF headtracked audio
Benz VR: Spatial Sound Design
(built for Desktop in UE4.27, FMOD and Reaper)
This prototype project takes the player on the journey of Bertha Benz as she brings the world's first motorcar to the attention of the world
Mathilde: Spatial Sound Design
(built for Desktop in UE4.26, FMOD and Reaper)
The goal of this project is to allow the player to explore the world of pioneering atonal composer Arthur Schoenberg as his estranged wife Mathilde, guided by audio (in particular music written by Schoenberg and letters written by Mathilde) during her love affair with artist Richard Gerstl which ended tragically.
Role of sound in Mathilde:
-
focus and guide the player's attention through the narrative
-
trigger progression between rooms based on player's discovery of letters
-
permit the player to enjoy Schoenberg's music in a dynamic non-linear way
-
mirror the degradation of the character's mental state as the experience progresses
Viking prototype: Sound Design
(built for Desktop in UE4.26, FMOD and Reaper)
This was a passion project in collaboration with a small group of programmers
Demonstrates:
-
interior and exterior convolution reverb
-
character movement sounds update with costume items
-
music composed specifically for project to enhance progression
-
dynamic weather sfx




